CSR Laws
You can read the information below in over 15 languages! Simply use the translation tool in the top-left corner of the screen to select your preferred language, including অসমীয়া, বাংলা, ગુજરાતી, हिन्दी, ಕನ್ನಡ, മലയാളം, मराठी, মৈতৈলোন্, नेपाली, ଓଡ଼ିଆ, ਪੰਜਾਬੀ, संस्कृतम्, தமிழ், తెలుగు, and اُردُو.
Got questions about CSR Laws? Ask them on the forum!
S.135 of Companies Act, 2013-Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
-
Every company having net worth of rupees five hundred crore or more, or turnover of rupees one thousand crore or more or a net profit of rupees five crore or more during any financial year shall constitute a Corporate Social Responsibility Committee of the Board consisting of three or more directors, out of which at least one director shall be an independent director.
-
The Board's report under sub-section (3) of section 134 shall disclose the composition of the Corporate Social Responsibility Committee.
-
The Corporate Social Responsibility Committee shall,—
-
formulate and recommend to the Board, a Corporate Social Responsibility Policy which shall indicate the activities to be undertaken by the company as specified in Schedule VII;
-
recommend the amount of expenditure to be incurred on the activities referred to in clause (a); and
-
monitor the Corporate Social Responsibility Policy of the company from time to time.
-
- The Board of every company referred to in sub-section (1) shall,—
-
after taking into account the recommendations made by the Corporate Social Responsibility Committee, approve the Corporate Social Responsibility Policy for the company and disclose contents of such Policy in its report and also place it on the company's website, if any, in such manner as may be prescribed; and
-
ensure that the activities in CSR Policy of the company are undertaken by the company.
-
- The Board of every company referred to in sub-section (1), shall ensure that the:
-
company spends, in every financial year, at least two per cent. of the average net profits of the company made during the three immediately preceding financial years, in pursuance of its Corporate Social Responsibility Policy:
-
Provided that the company shall give preference to the local area and areas around it where it operates, for spending the amount earmarked for Corporate Social Responsibility activities.
-
Provided further that if the company fails to spend such an amount, the Board shall, in its report made under clause (o) of sub-section (3) of section 134, specify the reasons for not spending the amount.
-
Schedule VII-See Sec 135
Activities which may be included by companies in their Corporate Social Responsibility Policies Activities relating to:
-
Eradicating hunger, poverty and malnutrition, [‘‘promoting health care including preventive health care’’] and sanitation [including contribution to the Swach Bharat Kosh set-up by the Central Government for the promotion of sanitation] and making available safe drinking water.
-
Promoting education, including special education and employment enhancing vocational skills especially among children, women, elderly and the differently abled and livelihood enhancement projects.
-
Promoting gender equality, empowering women, setting up homes and hostels for women and orphans; setting up old age homes, day care centres and such other facilities for senior citizens and measures for reducing inequalities faced by socially and economically backward groups.
-
Ensuring environmental sustainability, ecological balance, protection of flora and fauna, animal welfare, agroforestry, conservation of natural resources and maintaining quality of soil, air and water [including contribution to the Clean Ganga Fund set-up by the Central Government for rejuvenation of river Ganga].
-
Protection of national heritage, art and culture including restoration of buildings and sites of historical importance and works of art; setting up public libraries; promotion and development of traditional art and handicrafts;
-
Measures for the benefit of armed forces veterans, war widows and their dependents, 9[ Central Armed Police Forces (CAPF) and Central Para Military Forces (CPMF) veterans, and their dependents including widows];
-
Training to promote rural sports, nationally recognised sports, Paralympic sports and Olympic sports
-
Contribution to the prime minister's national relief fund 8[or Prime Minister’s Citizen Assistance and Relief in Emergency Situations Fund (PM CARES Fund)] or any other fund set up by the central govt. for socio economic development and relief and welfare of the schedule caste, tribes, other backward classes, minorities and women;
-
-
Contribution to incubators or research and development projects in the field of science, technology, engineering and medicine, funded by the Central Government or State Government or Public Sector Undertaking or any agency of the Central Government or State Government; and
-
Contributions to public funded Universities; Indian Institute of Technology (IITs); National Laboratories and autonomous bodies established under Department of Atomic Energy (DAE); Department of Biotechnology (DBT); Department of Science and Technology (DST); Department of Pharmaceuticals; Ministry of Ayurveda, Yoga and Naturopathy, Unani, Siddha and Homoeopathy (AYUSH); Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology and other bodies, namely Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO); Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR); Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) and Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), engaged in conducting research in science, technology, engineering and medicine aimed at promoting Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).]
-
- Rural development projects
-
Slum area development.
-
Disaster management, including relief, rehabilitation and reconstruction activities.
Note: only funds mentioned here are eligible for CSR contribution
Section 135 of Companies Act-changes effective Jan 2021
Paradigm shift in CSR regime-Spend or explain to Mandatory
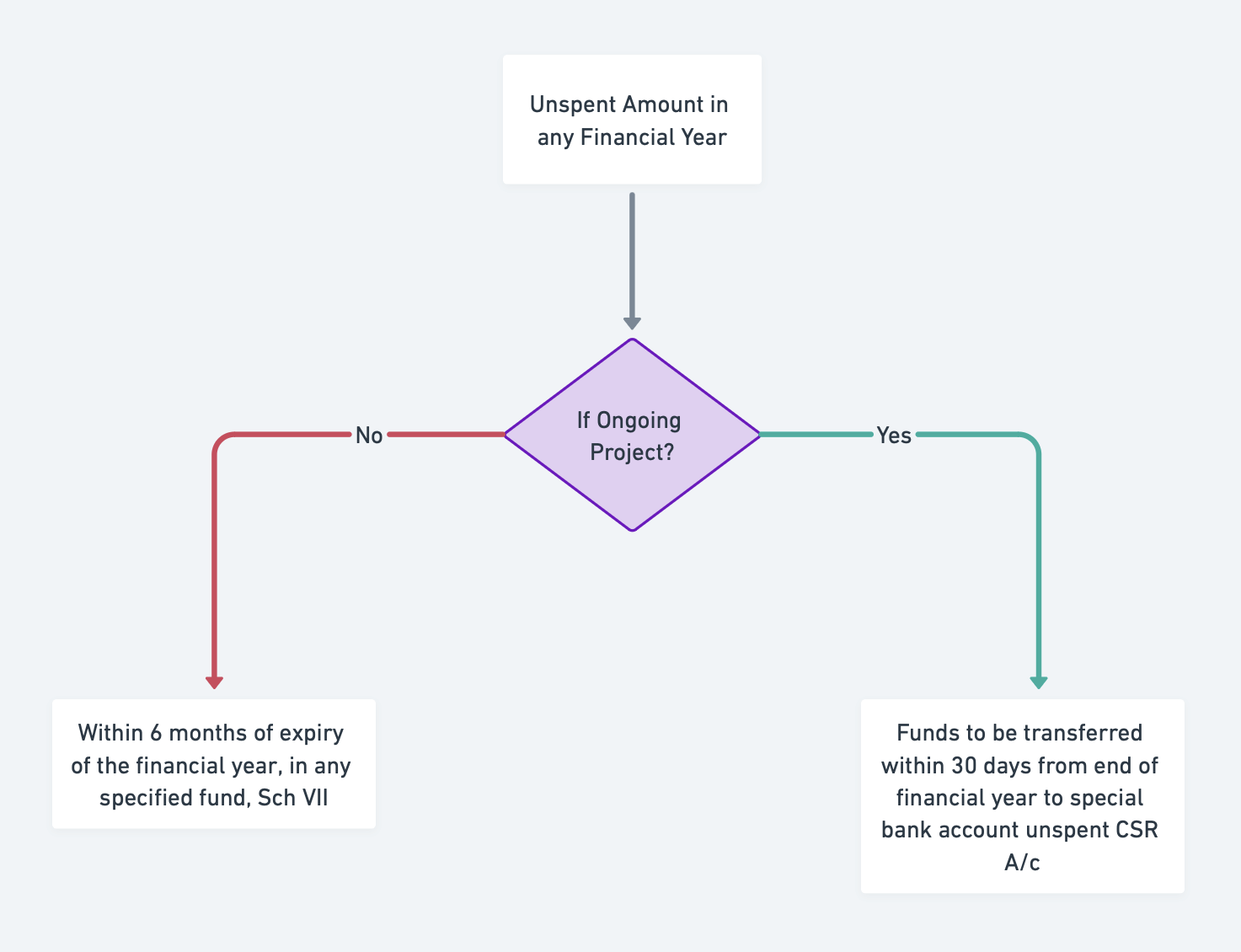
• Company fails to spend required CSR amount in any financial year,
a. The unspent amount is required to be transferred to any fund specified in Schedule VII, within a period of six months of the expiry of the financial year (in the case there is no ongoing project).
b. The unspent amount is to be transferred to a special account to be opened by the company in a scheduled bank to be called the unspent CSR account within 30 days from the end of the financial year (in the case of an ongoing project).
Such amount shall be spent on CSR activities within three financial years failing which the unspent amount is required to be transferred to any fund specified in Schedule VII, within 30 days.
Introduction of penal provisions: Penalty of twice the unspent CSR or INR 1 crore, whichever is less may be imposed on the company, and penalty of 1/10th of unspent CSR or INR 2 lakh, whichever is less may be imposed on all officers in default.
Illustrated:
Unspent Amount in any Financial Year:
- If Ongoing Project?
- Yes: Within 6 months of expiry of the financial year, in any specified fund, Sch VII
- No: Funds to be transferred within 30 days from end of financial year to special bank account inspect CSR A/c
Definition of CSR
Activities permitted under Section 135 of Companies Act 2013Exclusions:
-
Activities undertaken in pursuance of normal course of business of the company;
-
Contribution of any amount directly or indirectly to any political party under section 182 of the Act;
-
Activities benefiting employees of the company as per Code on Wages (apprentices not included)
-
Activities supported by the companies on sponsorship basis for deriving marketing benefits for its products or services;
-
Activities carried out for fulfilment of any other statutory obligations under any law in force in India.
Note-corpus donation, kind contribution, activities outside India except training of sports person is not CSR
Companies (CSR Policy) Rules 2021
Modes for undertaking CSR: CSR activities can now be undertaken by the company itself or through
-
Section 8 company/registered public trust/registered society-12A and 80G registration under Income-tax Act, 1961 established by the company, either singly or along with any other company, or
-
Section 8 company/registered trust/registered society established by the government; or
-
Any entity established under an Act of Parliament or a state legislature; or
-
Section 8 company/registered public trust/registered society, (with 12A and 80G registration under Income-tax Act, 1961) having an established track record of at least three years in undertaking similar activities.
URN and Form CSR-1
From 01 April 2021, every entity who intends to undertake any CSR activity, shall register itself with the Central Government by filing Form CSR-1 electronically with the Registrar of Companies (ROC).
-
On successful submission of Form CSR-1, a unique CSR Registration Number shall be generated by system automatically.
-
No timeline specified for registration. Only registered entities will be able to undertake CSR activity from 1.4.21
-
Applicable for 4 eligible entity types for getting CSR Funding
-
Following documents are required for filing Form CSR-1 on MCA portal:
- Copy of PAN Card of the NGO
- Details of Directors/BOT/Chairperson/CEO/Secretary/Authorised Rep
- Copy of Registration Certificate
- Digital Signature of the Authorised Person with his PAN Number
- Certification by Practising Professional
Companies (CSR Policy) Rules 2021
- Companies may now engage international organisations for designing, monitoring and evaluating the CSR projects and for capacity building of their personnel for CSR. Notified by CG under this Act.
- Administrative overheads have been defined and capped to 5% of total CSR expenditure. Admin OH means any expenditure for general management and administration for CSR function but designing, implementation, monitoring and evaluation of CSR projects will not be part of admin overheads
CSR Committee
- CSR Committee mandatory if CSR spend is more than Rs.50 lakhs in a year or there is unutilised CSR fund otherwise discharged by BOD
- The CSR Committee shall formulate and recommend to the Board, an annual action plan in pursuance of its CSR policy, which shall include the following, namely:
- the list of CSR projects or programmes that are approved to be undertaken in areas or subjects specified in Schedule VII of the Act;
- b the manner of execution of such projects/programmes as specified in rule 4;
- the modalities of utilization of funds and implementation schedules for the projects;
- monitoring and reporting mechanism for the projects or programmes; and
- details of need and impact assessment, if any, for the projects undertaken by the company:
- Annual Report format on CSR activities from 1.4.2020 (Annexure II) to be appended to the company AR-unspent, impact asstt. Admin OH, capital assets, location of CSR projects etc
Surplus arising out of CSR projects
- Any surplus arising out of the CSR activities shall not form part of the business profit of a company and shall be ploughed back into the same project or shall be transferred to the Unspent CSR Account and spent in pursuance of CSR policy and annual action plan of the company or transfer such surplus amount to a Fund specified in Schedule VII, within a period of six months of the expiry of the financial year.
- This means in case the project is income generating by way of fees etc., such income should be ploughed back into the same project but not form part of the business profit of the company.
Creation of assets from CSR expenditure
- The CSR amount may be spent by a company for creation or acquisition of a capital asset, which shall be held by:
- a company established under section 8 of the Act, or a Registered Public Trust or Registered Society, having charitable objects and CSR Registration Number under Rule 4(2); or
- beneficiaries of the said CSR project, in the form of self-help groups, collectives, entities; or
- a public authority:
- Provided that any capital asset created by a company prior to the commencement of the Companies (Corporate Social Responsibility Policy) Amendment Rules, 2021, shall within a period of one hundred and eighty days from such commencement comply with the requirement of this Rule, which may be extended by a further period of not more than ninety days with the approval of the Board based on reasonable justification.
- The asset will be transferred and the exp needs to be considered CSR exp
Visibility and UC by CFO
- Display of CSR activities on company website. The Board of Directors of the Company shall mandatorily disclose the composition of the CSR Committee, and CSR Policy and Projects approved by the Board on their website, if any, for public access.
- UC by CFO of the company that the CSR funds have been spent as per AAP not the CSR Committee
Carry forward and set off of excess spend
- Any excess CSR spend beyond requirement in a year can be set off in the next 3 FYs.
- Board resolution
Impact assessment
- Rule 8: Companies having an average CSR obligation of INR 10 crore or more in three immediately preceding financial years will be required to do impact assessment, through an independent agency
- CSR projects having outlays of INR 1 crore or more
- Completed not less than one year before undertaking the impact study.
- Ceiling 2% or Rs.50 lakhs per FY whichever is higher
- Cost to be budgeted in the year of undertaking impact assessment
Advisory by ICAI to companies to which CSR provisions apply (May 2020)
- ICAI has prescribed the format of auditors report and UC format to be issued by auditor for CSR funds implemented by NGOs/third party
- Advisory link: https://csr.icai.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/07/Advisory-for-Independent-Practitioners-Report-on-Utilization-of-CSR-Funds_hosted.pdf
CSR, ESG and Sustainability overlap
- Sustainability: The outcome achieved by balancing the social, environmental and economic impacts of business. It is the process that ensures that business goals are pursued without compromising any of the three elements (source: NGRBC).
- Sustainability is the umbrella for ESG (BRSR) and CSR, both are ways business demonstrate commitment to sustainable business practices.
- CSR is the starting point of ESG.
- CSR strategy can be refined to fit into ESG (BRSR) metrics.
- BRSR lends credibility to CSR by quantifying it.
Reporting compliance for corporates on Sustainability
- Form CSR 2
- Annual Action Plan (AAP)
- Annual CSR Report (Annexure II) appended to Board Report
- Business Responsibility Report (BRR)-discontinued
- Business Responsibility and Sustainability Report (BRSR)
- BRSR Core-July 2023- subset of BRSR requiring mandatory disclosure on select key performance indicators on ESG like upstream and downstream value chenin partners with reporting by 150 companies from 23-24 to all by 26-27 and guidelines for assurance providers
CSR 2-CSR Report
- Introduced in Feb 2022 effective 20-21
- Applicable to companies covered under 135(1)
- e CSR 2 information-(capture most details that we have covered in section 135 and required in Rules). It includes details of triggers, spend on ongoing and other than ongoing projects, unspent CSR amount, set off, assets created, impact assessment
- Filed within 30 days of holding of AGM as addendum to AOC 4
Journey of ESG (BRSR) in India
- In 2011, MCA issued the National Voluntary Guidelines (NVGs) on Social, Environmental and Economic Responsibilities of Business
- In 2012, SEBI mandated the top 100 companies (extended to 500 companies) by market cap submit BRR to report compliance with NVGs
- In 2017, SEBI recommended Integrated Reporting for BRR-together on financial and sustainable matters in single reporting
- In 2018, MCA issued national Guidelines on Responsible Business Conduct (NGRBC) to improve on NVGs
- In 2021, SEBI introduced improved BRRF requiring in form of BRSR applicable to top 1000 companies by m-cap from 22-23
Business Responsibility and Sustainability Reporting
NGRBC contain 9 principles and core elements
- Principle 1: Ethical Business Conduct-Businesses should conduct and govern themselves with integrity and in a manner that is ethical, transparent and accountable.
- Principle 2: Produced Responsibility-Businesses should provide goods and service in a manner that is sustainable and safe.
- Principle 3: Employee Welfare-Businesses should respect and promote the well-being of all employees, including those in their value chains.
- Principle 4: Stakeholder engagement-Businesses should respect the interests of and be responsive to all its stakeholders
- Principle 5: Human Rights-Businesses should respect and promote human rights.
- Principle 6: Environmental Responsibility-Businesses should respect and make efforts to protect and restore the environment.
- Principle 7: Public Policy Engagement-Businesses, when engaging in influencing public and regulatory policy, should do so in a manner that is responsible and transparent.
- Principle 8: Inclusive Growth-Businesses should promote inclusive growth and equitable development
- Principle 9: Consumer engagement-Businesses should engage with and provide value to their consumers in a responsible manner.
BRSR
- Each principle of NGRBC has core elements which enhance the operationalisation and objectivity of the principles
- BRSR is part of SEBI’s Listing Obligation and Disclosure Regulations (LODR)
- BRSR format:
- General information
- Management & Policy disclosures
- Principle wise performance disclosure-essential indicators and leadership indicators
- Voluntary BRSR permitted
Resources for new business for reference
Websites of corporates
- National CSR Portal https://www.csr.gov.in/content/csr/global/master/home/home.html
- National CSR eXchange https://www.csrxchange.gov.in
- MCA website
- FAQ by MCA attached with this PPT
For funding and proposal writing:
- NGOBox
- CSRBox
- Fundsforngos.org
- ProposalsforNGOs.com
- Devnetjobsindia.org
- Terravivagrants.org
- Tamuku
Websites of Ministries and Donors other than CSR
- Ngosindia.com
- Pandadoc.com
- Ngochrome.com
No Comments